
Diabetes is a common metabolic problem characterized by high glucose levels over a long period of time. It affects many people and has recently become a critical wellness issue.
There are several types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes, each with their own causes and treatment strategies. Effective treatment usually involves a combination of medications, dietary adjustments, regular exercise and monitoring of blood sugar levels.
Without proper treatment, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage and vision loss. But with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, people with diabetes can live healthy and fulfilling lives. In this comprehensive blog, we explore the causes, side effects, treatment options and safety measures for diabetes control.
Causes of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, each with its own causes:
Type 1 diabetes:

This type of diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this immune response is not yet known, but genetic and environmental factors are thought to play a role.
Type 2 Diabetes:

The most common form of diabetes, type 2 diabetes is often associated with insulin resistance, where the body and cells do not respond effectively to insulin. Genetic predisposition, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle and poor eating habits contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes:
This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and is thought to be caused by hormonal changes that affect insulin sensitivity. Women who are overweight, have a family history of diabetes, or are older than 25 are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow wound healing
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet.
It is important to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention when they occur, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications.
Treatment Options:
Insulin therapy:
People with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2 diabetes may need insulin injections to effectively control blood sugar.
Oral medications:
Medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors may be prescribed to lower blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity in people with type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle changes:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is essential to managing diabetes. This includes eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Blood sugar monitoring:
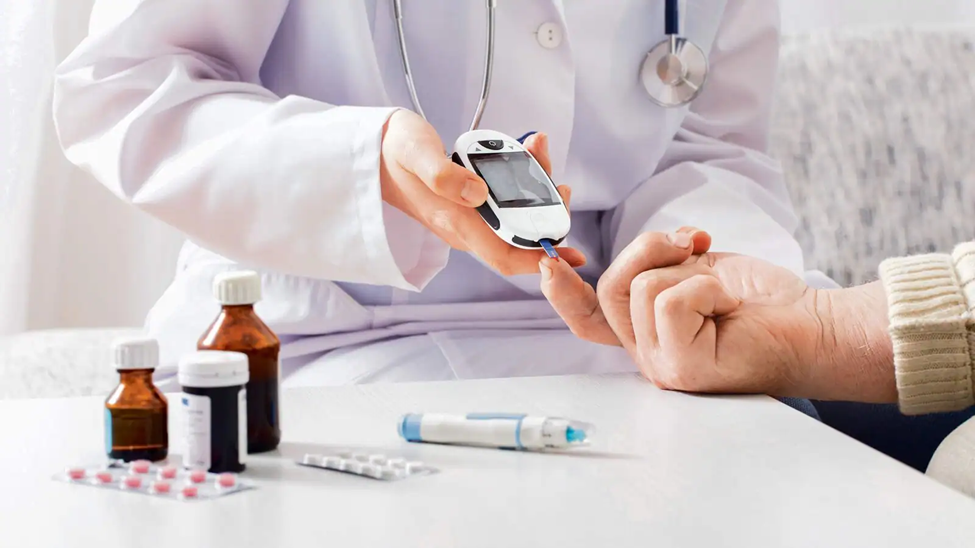
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for effective diabetes management. This helps people track their progress and make necessary changes to their treatment plan.
Precautions for Managing Diabetes
1 Follow Healthy Diet
An eating routine wealthy in natural products, vegetables, entire grains, and incline proteins can assist with managing glucose levels and forestall spikes.
2 Stay Active
Customary activity can further develop insulin responsiveness and assist with controlling glucose levels. Go for the gold 150 minutes of moderate-power practice each week.
3 Monitor Blood Sugar Levels:
Check your glucose levels routinely as coordinated by your medical services supplier and track the outcomes.
4 Take Medications as prescribed:
Adhere to your PCP’s guidelines with respect to drug measurement and timing to guarantee ideal control of your diabetes.
5 Manage Stress:

Elevated degrees of stress can influence glucose levels. Practice pressure decrease procedures like profound breathing, contemplation, or yoga to assist with overseeing pressure.
6 Attend Regular Checkups:
Timetable normal meetings with your medical services supplier to screen your diabetes and address any worries or difficulties instantly.
Latest Advances in Diabetes Research and Treatment
Advancements in Diabetes Diagnosis
Diagnosing diabetes has advanced significantly in recent years, as new screening methods and diagnostic tools have been developed that enable early detection of the disease. These advances include innovative technologies for measuring blood sugar, such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems that provide real-time information to help people control their glucose levels more effectively. In addition, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are used to improve the accuracy of diabetes diagnosis by analyzing complex data sets and identifying signs of the disease.
Emerging Therapies for Diabetes:
The field of diabetes care is rapidly evolving, and researchers are investigating new drugs and treatments to improve glucose balance and alleviate complications associated with the disease. One area of focus is the development of insulin analogs with improved pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles that provide more precise control of blood glucose while reducing the risk of hypoglycemia. In addition, there is increased interest in non-insulin drugs that target alternative pathways of glucose metabolism, and in innovative approaches such as gene therapy and stem cell-based therapies that hold promise for long-term management of diabetes.
Portioned medicine and personalized care:
Personalized medicine is revolutionizing diabetes care by tailoring treatment plans to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, metabolic characteristics, lifestyle factors and co-morbidities. Genetic testing and biomarker analysis allow health care providers to identify patients who may benefit from certain medications or interventions, while digital health technologies facilitate remote monitoring and personalized interventions. Precision medicine approaches allow healthcare professionals to optimize outcomes and improve quality of life for people with diabetes.
Advances in Diabetes Management Technologies:
Technological innovations have revolutionized diabetes management, providing patients with greater convenience, accuracy and control of the condition. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems have improved significantly in recent years, with sensors becoming smaller, more accurate, and able to transmit data wirelessly to connected devices. Closed-loop insulin delivery systems, also known as artificial pancreas systems, combine CGM technology with insulin pumps to automate insulin delivery and adjust the dose based on real-time glucose levels. In addition, mobile devices and smartphone apps allow people to monitor their blood sugar levels, track their diet and exercise habits, and receive personalized recommendations for effective diabetes management.
Targeting Diabetes Complications:
Prevention and treatment of diabetes-related complications are critical aspects of disease management and require a multifaceted approach that addresses cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, retinopathy, neuropathy, and other complications. Research efforts are focused on understanding the mechanisms behind these complications and developing targeted interventions to mitigate their effects. Multidisciplinary care teams work together to provide comprehensive care and support, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle changes, medication adherence and regular screening to prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes for people with diabetes.
Dietary and lifestyle interventions:
Dietary and lifestyle interventions play a central role in the management of diabetes by helping people achieve and maintain optimal glycemic control and reduce the risk of complications. Research has looked at various a In addition, mindfulness-based approaches and stress reduction techniques provide additional benefits by promoting emotional resilience and supporting mental health in people with diabetes.
Clinical trials and future directions:
Clinical trials are needed to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new therapies and interventions for the treatment of diabetes. They provide valuable information about new treatment strategies and shape the future of diabetes care. Ongoing research is exploring innovative approaches such as new drug therapies, medical devices, regenerative medicine techniques and digital health interventions that hold the promise of better outcomes and quality of life for people with diabetes. Patient participation in clinical trials is critical to advancing research and accelerating the translation of scientific discoveries into clinical practice, ultimately bringing us closer to the goal of finding a cure for diabetes.
Want To Know About Diabetes symptoms | Signs of all types of diabetes | Diabetes UK
Conclusion:
In summary, diabetes requires vigorous treatment that includes medication, lifestyle and regular monitoring. With informed guidance and proactive self-care, diabetics can reduce risks and maintain a high quality of life. Awareness, research and community support are essential in the ongoing fight against this common health problem.
Leave a Reply