
In the realm of automotive innovation, plug-in hybrids stand at the forefront, seamlessly blending the benefits of electric and gasoline propulsion systems. Unlike conventional hybrids that rely solely on gasoline engines supplemented by electric motors, plug-in hybrids offer the flexibility of charging their batteries from an external power source, such as a wall outlet or charging station.
This unique capability extends their electric driving range, allowing drivers to cover significant distances solely on electric power before seamlessly transitioning to gasoline power when needed.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of plug-in hybrids, exploring their unique features, environmental advantages, and the driving experience they offer. Whether you’re a seasoned car enthusiast or new to the world of eco-friendly transportation, join us as we uncover the exciting potential of plug-in hybrids.
What is a Plug-In Hybrid (PHEV)?

A plug-in hybrid vehicle (PHEV) combines an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and battery pack. Unlike traditional hybrid vehicles, which primarily rely on the combustion engine with occasional electric assist, PHEVs can be charged from an external power source and driven solely on electric power for a certain range before switching to hybrid mode.
The Advantages of Plug-In Hybrids:
1 Environmental Benefits:
Plug-in hybrids offer significant environmental advantages over conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. By incorporating electric propulsion, PHEVs produce fewer emissions and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to cleaner air and mitigating climate change.
2 Fuel Efficiency:
PHEVs typically achieve higher fuel efficiency than traditional vehicles, thanks to their ability to operate in electric mode for short distances. This allows drivers to reduce their reliance on gasoline and save money on fuel costs over time.
3 Range Flexibility:
Unlike fully electric vehicles (EVs), which are limited by battery range, plug-in hybrids offer greater flexibility and convenience for drivers. With the option to switch between electric and hybrid modes, PHEVs can cover longer distances without the need for frequent recharging.
4 Tax Incentives:
Many governments and local authorities offer incentives and tax credits to encourage the adoption of plug-in hybrid vehicles. These incentives may include tax rebates, reduced registration fees, and access to carpool lanes, making PHEVs an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers.
5 Enhanced Driving Experience:
Plug-in hybrids offer a smooth and quiet driving experience, particularly in electric mode. With instant torque delivery and responsive acceleration, PHEVs deliver impressive performance while reducing noise pollution and enhancing overall comfort for passengers.
6 Charging and Range:

One of the key features of plug-in hybrids is their ability to be charged from an external power source, such as a standard electrical outlet or dedicated charging station. Depending on the battery capacity and charging infrastructure available, PHEVs can typically be fully charged in a matter of hours, allowing drivers to maximize their electric range and minimize their dependence on gasoline.
In terms of range, plug-in hybrids offer varying levels of electric and hybrid driving capabilities. Some models may have a relatively short electric range of around 20-30 miles, while others can travel up to 50 miles or more on electric power alone. This range flexibility allows drivers to tailor their driving experience to suit their needs, whether commuting to work, running errands, or embarking on longer road trips.
How Plug-in-Hybrid Works?
Dual Power Sources:
Plug-in hybrid vehicles are equipped with two primary power sources: an electric motor and a gasoline engine. These two power sources work in tandem to propel the vehicle forward.
Electric Motor:
PHEVs have an electric motor that is powered by a high-voltage battery pack. This electric motor is responsible for driving the wheels and providing propulsion to the vehicle. It operates similarly to an electric vehicle (EV), drawing power from the battery to generate torque and propel the vehicle forward.
Battery Pack:
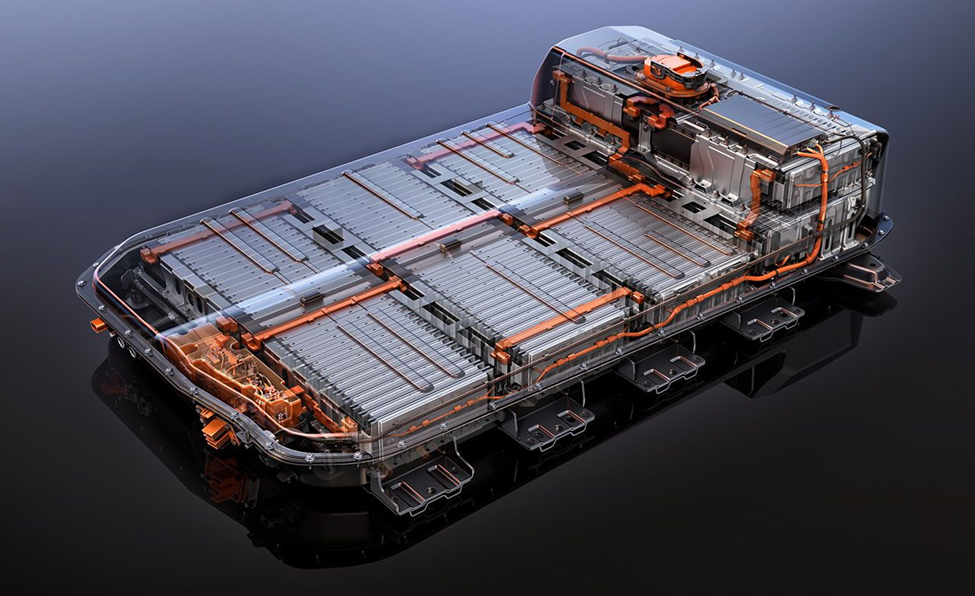

The high-voltage battery pack in a PHEV stores electrical energy to power the electric motor. These batteries are rechargeable and can be plugged into an external power source, such as a wall outlet or a charging station, to replenish their charge. The size and capacity of the battery pack vary depending on the PHEV model, but they typically provide enough energy to enable all-electric driving for a certain distance.
Charging:
PHEVs can be charged using external power sources. Owners can plug their vehicles into a standard electrical outlet or a dedicated charging station to recharge the battery pack. Charging times vary depending on factors such as the battery capacity and the charging power available. Some PHEVs also support fast charging, which allows for quicker replenishment of the battery’s charge.
Gasoline Engine:
In addition to the electric motor, PHEVs are equipped with a gasoline engine. This gasoline engine serves as a backup power source when the battery’s charge is depleted or when additional power is required, such as during high-speed driving or heavy acceleration. The gasoline engine can also charge the battery when necessary, acting as a generator to produce electricity.
Regenerative Braking:
PHEVs utilize regenerative braking technology to capture kinetic energy during braking and deceleration. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in the battery pack for later use, helping to extend the vehicle’s electric driving range and improve overall efficiency.
Powertrain Control System:
PHEVs feature sophisticated powertrain control systems that manage the operation of the electric motor, gasoline engine, and battery pack. These systems monitor driving conditions, battery charge levels, and power demands to optimize performance, efficiency, and emissions. They determine the most efficient mode of operation based on real-time data, seamlessly switching between electric-only, hybrid, and gasoline-only modes as needed.
If You Want To Know About How Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles (PHEV) Work
Examples of Popular Plug-In Hybrid Models:
1 Toyota Prius Prime:
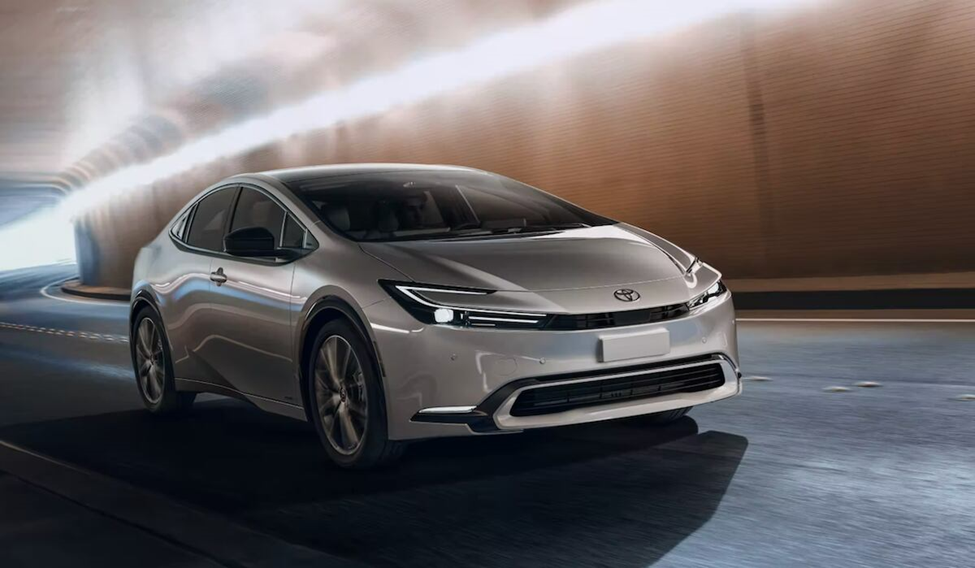

The Toyota Prius Prime is one of the most popular plug-in hybrids on the market, offering a spacious interior, impressive fuel efficiency, and advanced safety features.
2 Chevrolet Volt:
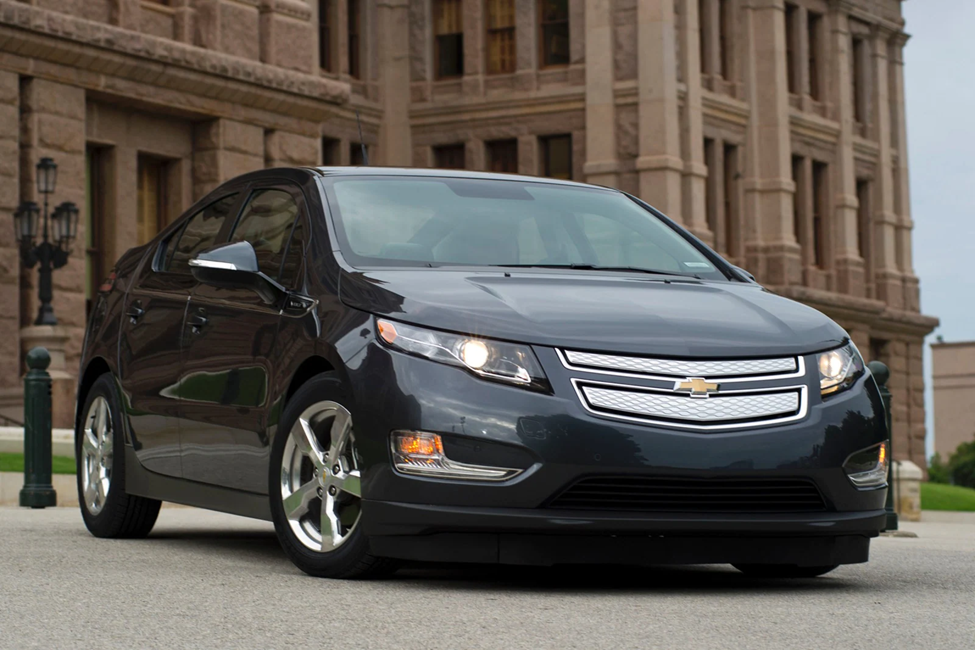

The Chevrolet Volt boasts a sleek design, responsive handling, and an electric range of up to 53 miles, making it an excellent choice for eco-conscious drivers.
3 BMW X5 xDrive45e:
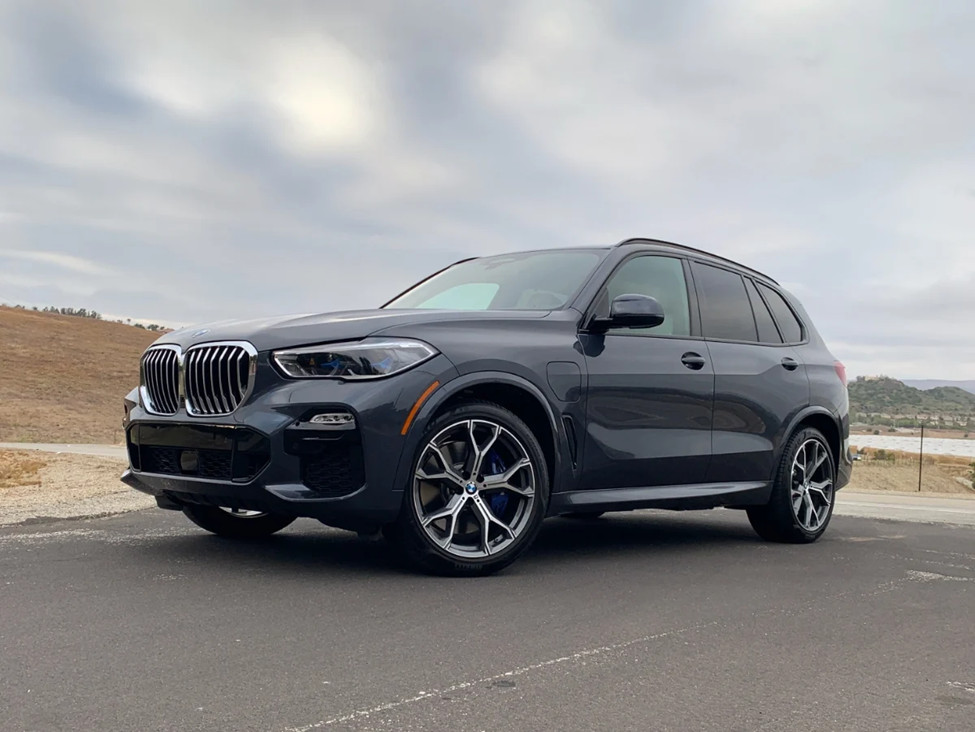

The BMW X5 xDrive45e combines luxury and performance with plug-in hybrid technology, offering a spacious interior, all-wheel drive capability, and an electric range of up to 30 miles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plug-in hybrid cars offer a compelling solution for drivers seeking a balance between environmental sustainability and practicality. With their ability to deliver impressive fuel efficiency, range flexibility, and enhanced driving experience, PHEVs represent a significant step forward in the transition towards a greener, more sustainable future. Whether you’re looking to reduce your carbon footprint, save money on fuel costs, or simply enjoy the thrill of electric driving, plug-in hybrids offer a versatile and compelling option for eco-conscious consumers.
Leave a Reply